The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) has forecasted a growth of 4% in the employment of anthropologists.
Anthropology is the study of humans from a cultural and biological perspective. Its broad studying topics ranging from the humanities to the sciences also give those who have degrees in anthropology a wide selection of careers to choose from. The graduate degree in Anthropology falls into the MA degree category and graduates get the title Master of Arts in Anthropology.
Anthropology is a competitive field with many graduates who go into the job market each year.
Salaries of those who are employed with a master’s degree in Anthropology are also over the average income, with a median annual salary of $63,190 in 2016.
If you are a recent graduate and are wondering “What can I do with a Masters in Anthropology?”, this article will attempt to walk you through the various career paths you can take.
The job positions that you can get with a Masters in Anthropology depend on several factors which we will go through in detail, such as:
- Specializations of Masters in Anthropology
- Previous Work Experience
- Current Skill Set
- Preferred Employer Type
- Chosen Career Path
After discussing each of these, we will also go through possible job positions you can get with a Masters in Anthropology as well as an important anthropological concept such as the semiotics theory.
Specializations Of Masters In Anthropology
Anthropology encompasses all aspects of human behavior and life so it is only logical that being a student of this subject will have you study a variety of topics within it. After having a general sense of anthropological concepts and research, students can choose any areas to explore in depth.
Some of the types of specializations for masters in anthropology include:
- Archaeology – tries to discover how people used to live in the past by finding and analyzing the remains of lost cultures and societies
- Biological Anthropology – studies the biological aspects of human and primate evolution and their interaction in society
- Business Anthropology – uses anthropological concepts to identify, analyze, and solve business problems which pertain to a company or corporation
- Environmental Anthropology – studies how the environment and its changes affect human life and interaction between cultures
- Forensic Anthropology – tries to connect and analyze human remains to find facts about any crime that has been committed
- Linguistic Anthropology – analyzes different linguistic systems of populations and tries to better understand its evolution and how language reflects social ties
- Medical Anthropology – is concerned with studying all factors that influence humans and their well being
- Museum Anthropology – uses concepts and methods of anthropology to study museums and their influence on human life
- Sociocultural Anthropology – which deals with how humans form cultures and societies and studies the way these cultures interact with each other
- Visual Anthropology – is concerned with the analysis of visual images to connect and explain human behavior in different societies
Each one of the specializations has a wide applicability. Based on which one you choose to study, there will also be a myriad of career opportunities that you can take to become successful in anthropological study.
Previous Work Experience
In order to have better career prospects, it is always a good idea to have some previous work experience in the field that you want to get a job in. For the Masters in Anthropology, since it is such a wide field, if you want to, for example find a job as a sociocultural anthropologist, it is recommended that you have some background in this particular field.
If you are a student who has completed their undergraduate and graduate degrees, one after the other with no breaks in between, you might not have had the chance to work and gain more experience. However, the way you can surpass this is by getting involved in internship, extracurricular, and volunteer/charity opportunities in your area of study.
By doing such activities, you get the following benefits:
- Build your resume
- Evaluate whether you want to work in that field in the long term
- Build a network
- Show potential employers that you were active in your field while studying
If you have had some work experience, you have already gained these benefits and have a clearer plan of what you want to do in the future. Your previous work experience will serve to make you stand out in potential job opportunities and help you get the position you want.
Current Skill Set
Another factor which influences job opportunities and positions for graduates of Masters in Anthropology is the skill set that they posses. Students who have completed their degrees, but have not gained any valuable skills will be less employable and will not be able to get involved in the job market after graduation.
That is why it’s immensely important that while you are studying for your degree, you are able to develop the necessary skills that jobs in anthropology require.
Some of these skills that you should have with a Masters in Anthropology while you are looking for a job are as follows:
- Communication Skills
- Critical thinking skills
- Problem solving skills
- Ability to develop research plans
- Ability to collect, analyze, and interpret data
- Statistical and quantitative skills
- Organization and planning skills
These are only a few of the skills you need to succeed in the job market as a graduate of anthropology. If you have already graduated and realize that you lack some of these abilities, then you have the opportunity to improve them by taking free online courses or joining clubs which work on improving employability.
Preferred employer type
Graduates with a Masters of Anthropology go into the labor market and take job positions in various sectors of the economy.
They can work in public, private, or non-profit organizations and take on roles in:
- Conservation work
- Heritage management
- Sales and marketing
- Advertising
- Health and social work
Most people have a preferred employer type that they would like to work for, so based on who you want to work with, your job prospects become narrower and you can determine where you want to become employed much easier.
Prospects.ac.uk in the United Kingdom has compiled a study about what sectors of the economy do Masters in Anthropology students work in.
They have found these results:
- 6% work in retail, catering, and bar work
- 2% work as secretarial and numerical clerks
- 11% work in business, finances and HR
- 5% are employed in legal jobs
- 7% work in other sectors
In addition, they have also determined that around 70% of recent anthropology graduates are employed in the first six months. This indicates that career prospects are favorable for masters in anthropology graduates and that they can find jobs in the sectors that they want.
Chosen Career Path
What ultimately decides the type of career and job position you will have is the chosen path within your field. Based on the scope of anthropological studies, there are four main career paths which graduates with a masters degree can follow.
Public sector careers
In the public sector, anthropologists work for the government and have various responsibilities. They deal with research and planning, as well as managing people. They use their skills of analysis to work in departments for legislation, cultural heritage, police departments, health management, natural resource management and so on. With most anthropologists going into academia, the government is the second largest employer of people with a masters degree in anthropology.
Private sector careers
Anthropologists are also demanded in the private sector in various businesses. They possess great research skills so they are employed in research and development, market research, planning and organizing marketing strategies, as well as finding out consumer perspectives on products and services.
Non-profit sector
The third sector is also a great place for anthropologists to become involved in. They help non-governmental and non-profit organizations to make an impact in the community through research and planning. They design initiatives and programs which improve the lives of people based on their understanding of the interaction of societies and cultures.
Academic Careers
Finally, the largest employer of anthropologists is academic. Those with a masters in anthropology go on to conduct research and collect data for various topics in universities and research departments. They write and publish papers in reputable journals and if they want to also become involved in teaching, they go on to complete their PhD in Anthropology. With the added qualifications, they teach in colleges and universities while continuing to publish their research.
Common Job Positions
Now that we have explored the factors which influence your choice of career as a graduate with a masters in anthropology, we can go through some common job positions that people with this qualification take.
Here are 5 job positions and their descriptions for Masters in Anthropology.
Local Government Officer
Local Government Officers work in the public sector to make sure that services in states and local governments are delivered effectively. They coordinate activities and events, provide policy formulation and evaluation services, communicate with stakeholders, and manage the local government staff.
Community Development Worker
This position works with members of different communities to identify and solve any problems that they might have. They actively communicate with key members and stakeholders, analyze data, prepare and implement action strategies, and then evaluate their impact. In addition, they manage community funds as well as recruit and train staff.
Charity Officer
Charity Officers work with NGOs and the community to develop projects and find funding for them. They write proposals and identify donors who are willing to sponsor events and programs, organize meetings and maintain contact with them to report the impact of the initiatives.
International development worker
In this job position, you will be working with communities in developing countries to identify their needs, develop programs which would potentially solve problems, implement them, and then evaluate their impact. This could be in various sectors, starting from basic health education, and business.
Cultural Resource Manager
This job position could be in public or non-governmental sectors. Cultural Resource Managers evaluate cultural heritage and develop plans on how to manage and preserve them. They could be responsible to manage teams of people and organize various educational tours and visits, as well as advocate for better conservation methods of important historical sites.
Besides these six job positions, there are other ones that you can take with your qualifications.
These include:
- Museum Curator
- Social Worker
- Human Resources Officer
- Mass Communication
- Ethnographer
- Management Consultant
- Humanitarian Officer
- Policy Analyst
- Urban Planner
- Environment and Natural Resources Officer
Semiotics Theory
Semiotics is an important concept in anthropology, which students need to have developed by the time they graduate with a masters degree. It will help you immensely to know the details and what the theory is about.
Semiotics is the relationship between signs, objects, and meaning. It is the study of how humans understand and relate different objects and signs to various interpretations.
There are three branches of semiotics:
- Semantics
- Syntactics
- Pragmatics
Each of these branches studies how signs relate to their interpretation, with each other, and with what effect they have on humans. One of the tools through which semiotics is analyzed is by using the Greimas Semiotic Square, pictured below.
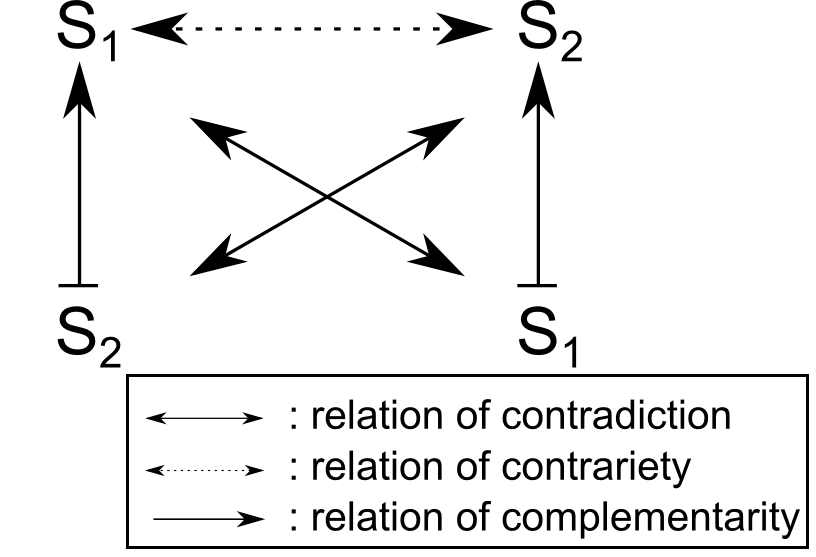
The square analyzes the meaning and structural relationships of signs with each other and their interpretation. Based on it, there are 6 types of structures, each one with their individual relationship elements, denoted by S in the figure.
| Structure Type | Relationship | Elements |
| Schema 1 | Contradiction | S1 + ~S1 |
| Schema 2 | Contradiction | S2 + ~S2 |
| Deixes 1 | Implication | ~S2 + S1 |
| Deixes 2 | Implication | ~S1 + S2 |
| Complex | Contrary | S1 + S2 |
| Neutral | Contrary | ~S2 + ~S2 |
Semiotics is important in linguistics and its analysis, how anthropologists study societies and cultures, and in other areas of study of anthropology.

